Financial education for life
Understand, apply, connect – the Erste Financial Life Park imparts financial knowledge, explains economic and financial interrelationships and strengthens skills for future-oriented action.
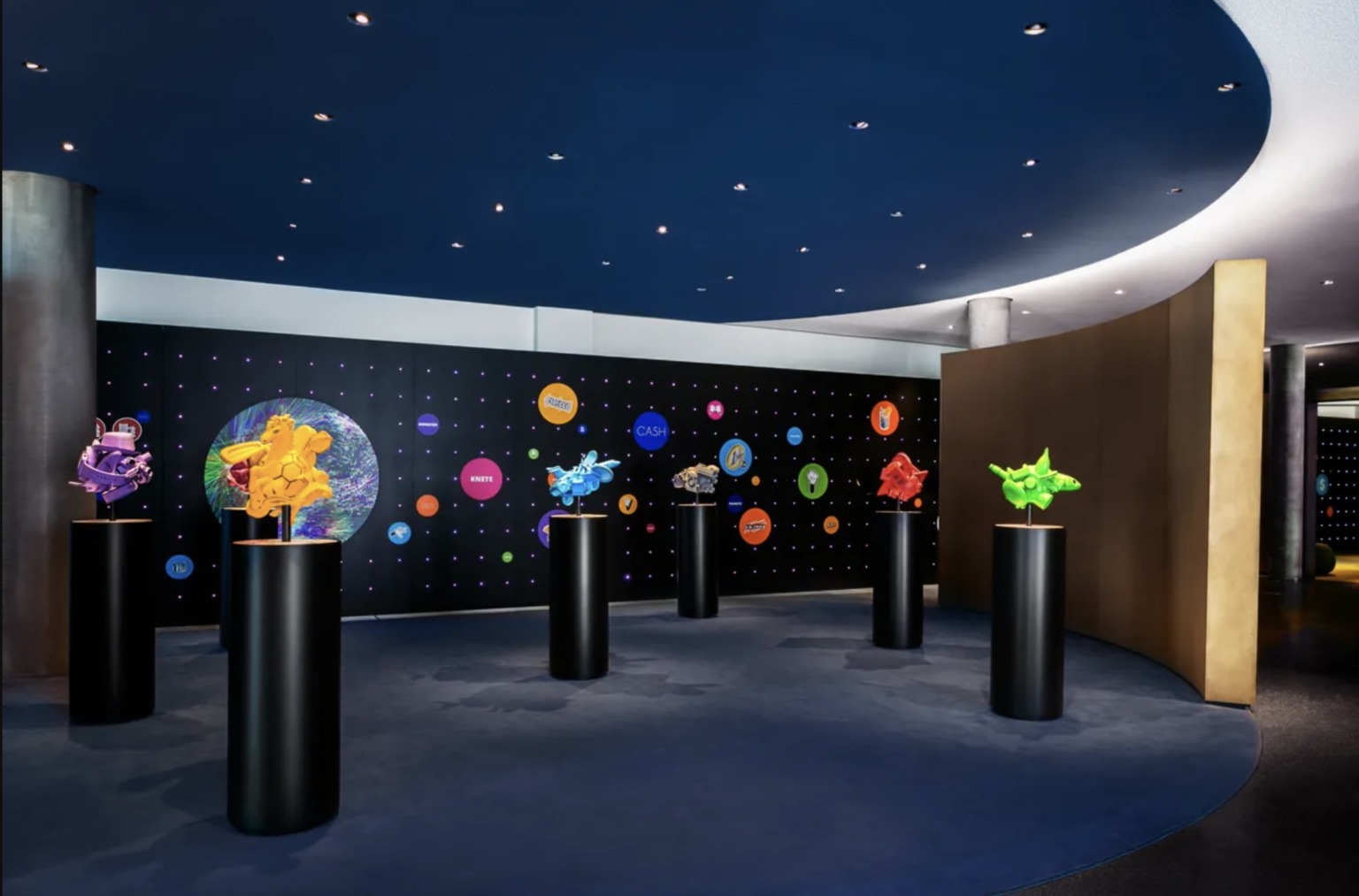


What is FLiP?
The Erste Financial Life Park, or FLiP for short, is Austria’s most prominent financial education project.
FLiP offers guided interactive tours that promote financial literacy and the importance of finances for personal life planning in a fun and interactive way.
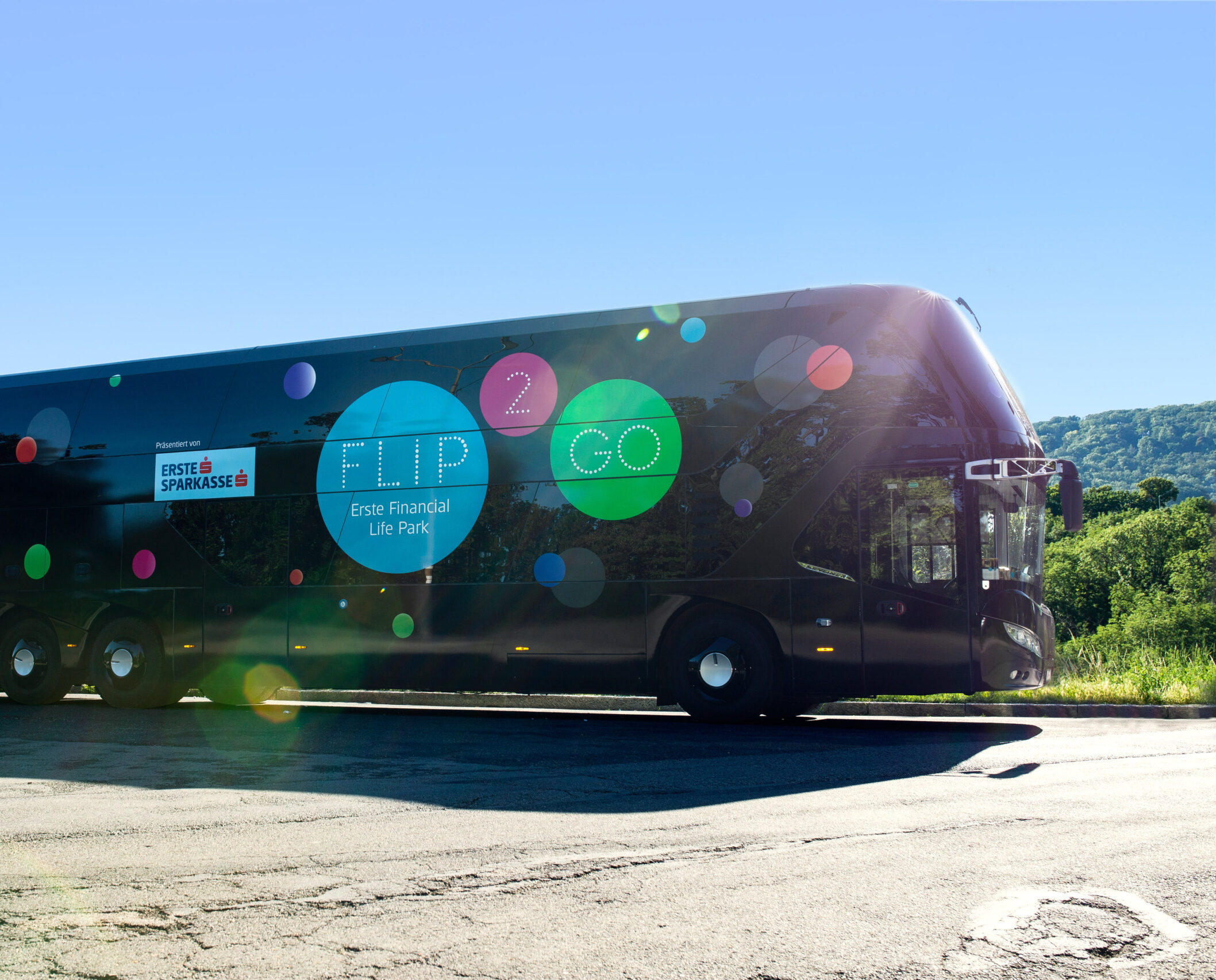

FLiP2Go
A visit to FLiP is not possible? No problem! Our financial education bus, FLiP2Go, goes around Austria and stops at schools. The programme is aimed at children and young people aged 10 and above.
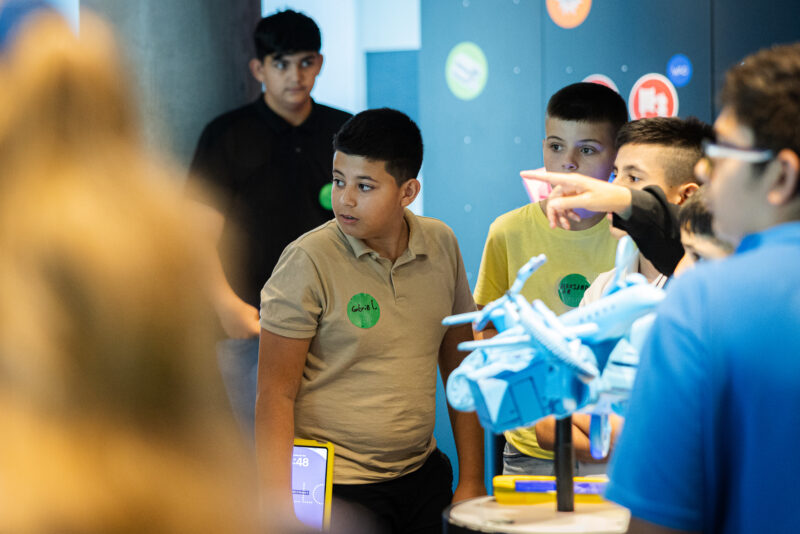

FLiP Tour

FLiP Focus Tours
Projects and Initiatives
FLiP’s aim is to impart financial knowledge – free of charge and accessible to everyone.
That’s why, in addition to our tours, we offer the FLiP App, teaching materials and other exciting projects and initiatives.

Teaching materials
We provide teaching materials on financial and economic topics – available to download free of charge!
Some of our teaching materials cover the topics discussed during our FLiP tours, which is why they are ideal for preparing for or following up on visit with us.
Subscribe to our newsletter*!
subscribe for new tour dates and important updates.
*only available in German











